| |
Diseases of Vegetables - Pea | |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| | Downy Mildew | Ascochyta Leaf and Pod Spot and Foot Rot | Mycosphaerella Blight | Powdery Mildew | Root Rot and Yellows | Seed Rot | Aster Yellows | Pea seed-borne Mosaic virus | Stunt | Bean Yellow Mosaic virus
Downy Mildew.
Peronospora viciae - pod infection
What to look for?
This disease is favored by cool wet growing conditions. Oospores over-winter in seed and crop residues. Seed or seedling infection results in systemic damage and death of infected plants. Plant to plant infection results in a grayish mold on the undersides of infected leaves as well as pod invasion by the mycelium. While this disease does exist in Alberta, levels of infection above 5% of the crop are unusual.
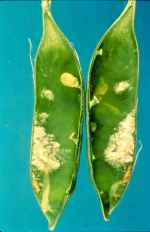
Photo: Howard | Picture description
Downy mildew inside the pod. |
.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Garfish mold on leaf underside. |
.
Management strategy
Crop rotation, seed treatment and burial of infected crop residues are control procedures. Disease levels of 30 to 50% of the stand have occasionally occurred but there is no economic control at present.
Ascochyta Leaf and Pod Spot and Foot Rot
Ascochyta pisi
What to look for?
Ascochyta pisi, Mycosphaerella pinodes and phoma medicagenis (Mycosphaerella and Ascochyta) all can infect peas and produce infections that appear similar to one and another. All three are seed-borne and Mycosphaerella and Phoma are residue-borne and in fact vigorous saprophytes.

Photo: Evans | Picture description
Mycosphaerellium lesions on the pod surface. |
.
Management strategy
Seed treatment and a 3 - 5 year crop rotation and foliar fungicides will give disease control.
Mycosphaerella Blight.
Mycosphaerella pinodes
What to look for?
Mycospharella blight can cause seedling death. Both Mycospharella and Phoma medicagenis produce resting sclerotia, and chlamydospores which allow for long term soil survival.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Seedling killed by the blight fungus. |

Photo: Morrall | Picture description
Pod damage to the peas will often result in discoloured green or yellow peas that are downgraded for livestock feed. |
.
Management strategy
None
Powdery Mildew.
Erysiphe polygoni
What to look for?
Powdery mildew is widespread in peas but not often very destructive. Mildew is not favoured by wet, rainy, windy weather but by relatively dry somewhat humid conditions. Heavy infestations of powdery mildew will often impede the drying of the swathed crop that is intended for seed.

Photo: Morrall | Picture description
Powdery mildew covers all parts of the pea plant from tendrils to stems. |

Photo: Evans | Picture description
Heavy mildew infection. |
.
Management strategy
There are resistant varieties available but few are in commerce. The mildew infection is most obvious on late planted peas in any given growing area. Normally peas mature before the disease becomes significant.
Root Rot and Yellows.
Fusarium solani and Pythium sp.
What to look for?
Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi is a destructive seed- and soil-borne pest of peas. Many backyard gardens in Alberta cannot grow peas because of the build-up of this pathogen in the soil over very many years. Fusarium infection does not cause root blackening. In fact, the roots are healthy but a red or yellow discoloration extends into the stem causing the mount to turn yellow from the ground upwards finally causing plant death.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Dead and dying maturing pea plants. |

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Fully wilted pea plants. |
.
Management strategy
Pythium spp. and its related Aphanomyces spp. can cause considerable damage to seedling pea stands. Pythiums are favored by high soil moisture and high temperature, and Aphanomyces by high soil moisture and low temperature. Seed treatment and crop rotation are important control procedures as well as avoidance of wet or low lying soils prone to flooding.
Seed Rot.
Rhizoctonia solani
What to look for?
Wet soils high in organic matter favor Rhizoctonia infection particularly in the west. The leafless peas developed in the UK in the 1960's have turned many diseases, including bacterial and Sclerotinia spp. infections and losses into relatively minor problems. The vastly improved standability and crop air circulation due to the leafless nature of the crop, have allowed peas to thrive exceptionally well on the prairies.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Severely damaged pea seeds. |
.
Management strategy
None
Aster Yellows.
Virus
What to look for?
Aster yellows type diseases show up sporadically or rarely in peas. The phyllody in peas is likely related to clover phyllody.

Photo: Pepin | Picture description
No flowers or pods with lots of distortion. |
.
Management strategy
None
Pea Seed-Borne Mosaic Virus.
Pea Seed-Borne Mosaic Virus
What to look for?
This virus has now been controlled by certification. Up to 30% seed-borne incidences have occurred. Aphids transmit this virus. If pea crops are performing poorly, check for this virtually symptomless virus.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Virus infected pea vines (symptomless). |
.
Management strategy
Grow virus-free seed.
Stunt.
Virus
What to look for?
Pea stunt occasionally shows up when peas are grown proximal to clover crops. This is an aphid-borne virus that is not seed-borne in peas.

Photo: Howard | Picture description
Stunted pea plant. |
.
Management strategy
None
Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus.
Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus
What to look for?
Bean yellow mosaic can spread rapidly in this crop in years of high aphid infestations. It is seed transmitted in fava bean (up to 5%) and may occur naturally in wild legumes. It is not seed transmitted in peas.

Photo: Evans | Picture description
Typical mosaic pattern. |
.
Management strategy
None
Go to Diseases of Field Peas for more information on diseases of peas.
Photographs and information assembled and prepared for ARD by Dr. Ieaun R. Evans Agri-Trend Agrology Ltd. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Other Documents in the Series |
|
| |
Diseases of Vegetables
Diseases of Vegetables - Carrot
Diseases of Vegetables - Celery
Diseases of Vegetables - Corn
Diseases of Vegetables - Cucumber
Diseases of Vegetables - Garlic
Diseases of Vegetables - Lettuce
Diseases of Vegetables - Muskmelon
Diseases of Vegetables - Onion
Diseases of Vegetables - Parsnip
Diseases of Vegetables - Pea - Current Document
Diseases of Vegetables - Zucchini
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
For more information about the content of this document, contact Robert Spencer.
This information published to the web on November 26, 2003.
Last Reviewed/Revised on December 4, 2012.
|
|