| | Introduction | More information
Introduction
The Agricultural Operation Practices Act (AOPA) includes requirements for managing manure and siting new and expanding livestock operations in Alberta. The legislation was amended in 2002 after consultations with the agriculture industry and other stakeholders. Further amendments were made in 2004 based on experience gained with the legislation. On January 1, 2005, all manure application, record keeping and soil test requirements came into full effect.
Alberta Agriculture, Food and Rural Development (AAFRD) is responsible for developing and updating the legislation and also takes a lead role in education and technology transfer. The Natural Resource Conservation Board (NRCB) administers the legislation pertaining to the siting of confined feeding operations (CFOs), and monitoring and enforcement of standards for all livestock operations in Alberta. This objective of this paper is to describe manure management requirements for livestock operations in Alberta under AOPA.
Manure application
Anyone applying manure or compost (including composting materials) to land must take into account:
- Soil nutrient limits;
- Soil type;
- Incorporation requirements; and,
- Setback distances to neighbours and common bodies of water (including the bed and shore of rivers, creeks, canals, lakes and sloughs).
Anyone spreading manure or compost must only apply to arable land and apply at least:
- 30 m from a water well;
- 10m from common bodies of water for subsurface injection;
- 30m from common bodies of water for surface spread and must incorporate it within 48 hours of application, except for on forage, direct-seeded crops, frozen or snow covered land; and,
- 150 m from a residence or occupied building if it is not incorporated within 48 hours (e.g. on forage, direct-seeded crops, or frozen or snow covered soils).
It should be noted that grazing livestock are not subject to the setback requirements under AOPA.
Manure application to forage, direct-seeded crops, or frozen or snow covered soils
The slope of the land determines the minimum setback distances required when spreading manure or compost on forage, direct-seeded crops, or frozen or snow covered soil (Figure 1):
- Where the slope is less than 4 percent, manure or compost materials may not be applied within 30m of a water body;
- Where the slope is between 4 and 6 percent, manure or compost materials may not be applied within 60m of a water body;
- Where the slope is between 6 and 12 percent, manure or compost materials may not be applied within 100m of a water body;
- Where the slope is greater than 12 percent, no manure or compost application is permitted.
Operations with more than nine months of manure storage capacity must obtain approval from the NRCB to spread manure or compost on frozen or snow-covered ground.
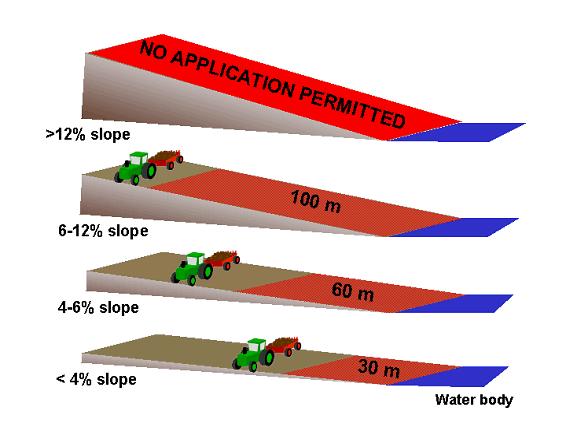
Figure 1. Prescribed setbacks from water bodies when applying manure or compost on forage, direct seeded crops or frozen or snow-covered soil.
Soil nitrate-nitrogen limits for manure application
The amount of manure or compost applied must not increase soil nitrate-nitrogen levels above the limits specified in table 1. (0 to 60 cm depths)
Table 1. Soil nitrate-nitrogen limits for agricultural soils prescribed under the Agricultural Operation Practices Act
 | Soil Texture |
| Soil Type | Sandy
(>45% sand and water table < 4m) | Sandy
(>45% sand and water table > 4m) | Medium and Fine Textured |
| Brown | 80 kg/ha
(75 lbs/ac) | 110 kg/ha
(100 lbs/ac) | 140 kg/ha
(125 lbs/ac) |
| Dark Brown | 110 kg/ha
(100 lbs/ac) | 140 kg/ha
(125 lbs/ac) | 170 kg/ha
(150 lbs/ac) |
| Black | 140 kg/ha
(125 lbs/ac) | 170 kg/ha
(150 lbs/ac) | 225 kg/ha
(200 lbs/ac) |
| Grey wooded | 110 kg/ha
(100 lbs/ac) | 140 kg/ha
(125 lbs/ac) | 170 kg/ha
(150 lbs/ac) |
| Irrigated | 180 kg/ha
(160 lbs/ac) | 225 kg/ha
(200 lbs/ac) | 270 kg/ha
(240 lbs/ac) |
Source: Table 3, Schedule 3, Standards and Administration Regulation, Agricultural Operation Practices Act
Producers must have access to sufficient land base to handle a one-time application of manure or compost based on the nitrogen limits.
Soil salinity limits for manure application
Manure must not be applied if the soil salinity is more than 4 deciSeimens per metre (dS/m) and the amount of manure or compost applied must not increase the salinity by more than 1 dS/m as measured by electrical conductivity at 0 to 15 cm unless it is a benefit to the soil as approved by the NRCB.
Record keeping
Anyone who handles, applies, or receives more than 500 tonnes of manure or compost per year must keep records and conduct soil tests where it is applied. These requirements apply to custom manure applicators, producers spreading manure on land, and anyone who receives over 500 tonnes of manure or compost annually. Anyone handling less than 500 tonnes is not required to keep records or soil test, but must respect the manure application limits and setbacks.
Records must be kept for a minimum of five years, but do not need to be submitted unless requested by the NRCB. The records required include soil test results for the areas that manure is applied, the amount of manure or compost produced, applied or handled, and the date, name and address of a person who receives or applies manure or compost.
Soil testing and analysis
Soil testing is only required for operations that handle over 500 tonnes of manure or compost annually. Soil tests do not have to be conducted every year for each manure or compost application if the soil nitrogen and salinity limits will not be exceeded by the application. However, the soil test results cannot be older than three years except for soil texture, which is a one-time analysis.
Nutrient Management Plans
Not all producers require nutrient management plans for applying manure to land. Only if a person does not have sufficient land base to meet the nitrate-nitrogen limits as required in AOPA or wants to apply manure on saline soils, must they obtain authorization from the NRCB by completing an actual nutrient management plan. For the purpose of AOPA, nutrient management plans only need to deal with soil nitrate-nitrogen and salinity limits.
More Information
Alberta Agriculture Ag-Info Centre: 1.866.882.7677, AAFRD website (Type “AOPA” in the search option or click on Livestock, Livestock Production, AOPA)
For publications call: 1.800.292.5697
Natural Resource Conservation Board (NRCB)
Dial 310.0000 first for a toll free connection
| Lethbridge | Ph: 403.381.5166 |
| Red Deer | Ph: 403.340.5241 |
| Morinville | Ph: 780.939.1212 |
| Fairview | Ph: 780.835.7111 |
Queen’s Printer Bookstore: 780.427.4952
Morris Seiferling and Phil Boehme
Technical Services Division, Alberta Agriculture, Food and Rural Development, Edmonton and Red Deer, AB
Tel: (403) 340-5851
Email: phil.boehme@gov.ab.ca |
|