| | Alberta's Rat Control Program Main Page
.
Rat Control Methods
Rat infestations can be prevented by any of three methods: food source removal, rat shelter removal, rat proofing.
Food Source Removal
Rats are capable of eating almost anything. It is important to remove all possible food items such as garbage, empty food containers, spilled grain or feed. Keep pet food secure and clean up uneaten food. Keep domestic garbage in containers until disposed of. Properly maintain any garbage pit or compost pile you may have. Do not give rats a chance. Remove any and all possible food sources.
Remove Rat Shelters
Rats can and will make any object their temporary or permanent home as long as they can crawl underneath. Until a rat can seek out permanent cover, it will use any flat object lying on the ground including tires, planks, square bales, junk, etc. Keep your property clean and tidy.
Rat Proofing
Buildings with cement foundations and floors, as well as metal siding, help eliminate rat habitat. By elevating farm out-buildings, protecting doorways and windows, using cement floors for sheds, granaries, warehouses and industrial structures, rats can be successfully turned away from potential shelter. Efficient rotation of stored grain or forage bales will also discourage rat activity.
 
Rat chewing is evidence of rat infestations.
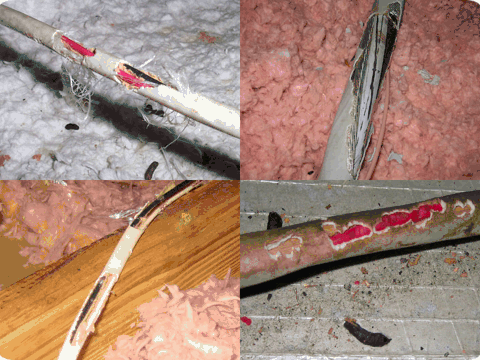
Electrical wire damage due to rats chewing.
Use of Poisons
- The most common and most effective rat bait used today is anti-coagulant bait that causes death in one to three days by painless internal bleeding.
- Pre-mixed anticoagulant rat bait in oats groats, pellets or blocks, or in concentrated form for water baiting are the most suitable rat baits for Alberta.
- They are also one of the safest rat baits in use today. Some anticoagulant rat bait may require several feedings to produce death.
- Newer rat baits such as bromodialone, brodifacoum difethialone require only a single feeding to kill rats but are less safe to non-targets, such as pets and livestock, than multiple feeding baits. The newer baits still require up to three days of consumption to kill rats. For safety reasons, only multiple feeding rat bait should be used near occupied buildings and all outside baiting needs to be placed in approved bait stations.
- Always use appropriate baits. Use dry bait (oat groats, pellets or block) where moisture or water is available, and water bait (Liquatox water soluble bait) in dry conditions. Rats can obtain daily moisture requirements from solid foods such as grain, green feed, and even packed and covered garbage.
- First aid and antidote treatment appear on all rat bait container labels.
Baiting Strategies
Proper placement of rat bait will ensure maximum results.
- Place bait where rats will find it easily.
- Place bait in all potential rat habitat in secure bait stations or where children, pets, and non-targets cannot access it.
- Keep fresh bait out at all times as long as rat activity is seen or suspected.
- Set bait in obvious rat habitat such as bale stacks, under granaries, barns, shelters, silage pits, abandoned buildings, nuisance grounds, and garbage facilities.

Tier 1 bait stations at a landfill set up for preventative control of rats. |
|